BBEX Exoskeleton: Advanced Support Technology Based on Spinal Biomechanics for Multidimensional Force Assistance
In modern industrial and high-intensity labor environments, repetitive lifting often leads to damage to the spine and back muscles, particularly lumbar injuries. This issue is prevalent in workplaces and has garnered widespread attention. To address this challenge, exoskeleton technology has been developed to provide effective support, reduce physical strain, and improve work efficiency.
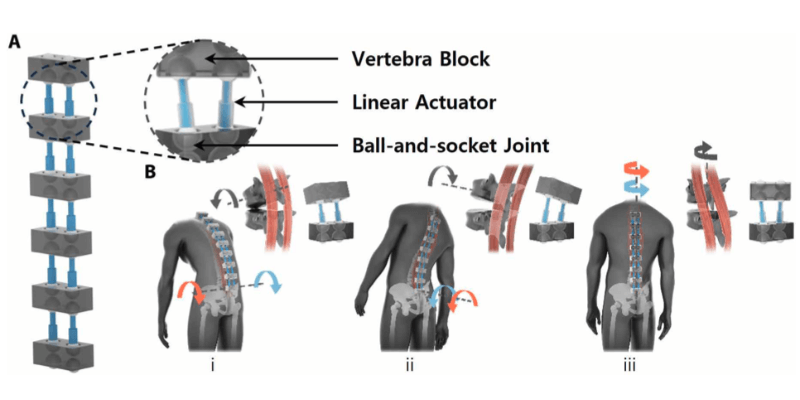
The human spine is a complex biomechanical structure composed of multiple vertebrae and intervertebral joints, capable of multi-degree-of-freedom movement. Each intervertebral joint consists of an intervertebral disc and two pairs of facet joints, with the disc absorbing shock and the facet joints controlling the spine's flexion and rotation. This structure provides the spine with flexibility in three degrees of freedom: extension-flexion, lateral bending, and axial rotation. The erector spinae muscles, located along the spine, work closely with the spinal anatomy to assist in various movements, crucial for coordinating the spine's multi-degree-of-freedom movements, especially during asymmetric lifting.
A research team from Seoul National University has recently introduced the Active Bilateral Back Extensor Exoskeleton (BBEX). Although exoskeleton technology itself is not new, BBEX brings innovative improvements in design and functionality, particularly in simulating the spine and back extensors, aiming to enhance existing back support devices.
Technical Features
Biomechanical Simulation: The BBEX exoskeleton uses a multi-degree-of-freedom design, incorporating serial linear actuators to mimic the natural structure and movement patterns of the spine and back extensors. This design allows the exoskeleton to provide multidirectional force support, accommodating various asymmetric lifting tasks.
Support and Comfort: By accurately simulating the function of the erector spinae, BBEX provides natural support during high-intensity tasks, reducing pressure on the spine. Its design is intended to coordinate with the natural movement of the human spine, enhancing comfort and effectiveness.
Multidimensional Force Support: BBEX is equipped with a Secondary Erector Spinae Mechanism (SES), consisting of a series of connected drive modules, including vertebral blocks, ball-and-socket joints, and linear actuators, to simulate the bilateral configuration of the erector spinae. This mechanism enables similar three-degree-of-freedom rotation as the human spine, providing effective multidimensional support during lifting, reducing the force demand on back muscles, and lowering joint pressure on the spine, particularly in cases where back muscle force primarily generates joint shear forces. The assistive force effectively mitigates these forces.
Safety Verification: Despite the innovative aspects of BBEX, safety verification remains crucial. The device has undergone rigorous testing to ensure its stability and reliability in practical applications.
Application Prospects
BBEX exoskeleton offers a broad range of potential applications, including:
Industrial Environments: In sectors such as construction, manufacturing, and warehousing, BBEX can help workers reduce their burden and increase work efficiency.
Rehabilitation Therapy: In the medical field, BBEX's support and assistance functions can aid patients in regaining mobility and improving their quality of life.
Other Applications: In high-intensity tasks such as military and rescue operations, the additional force support provided by BBEX also holds potential value.
Conclusion
The Active Bilateral Back Extensor Exoskeleton (BBEX) represents a significant advancement in exoskeleton technology. By precisely simulating the biomechanical characteristics of the spine, BBEX demonstrates new possibilities in providing multidimensional force support. Through this innovative technology, the research team from Seoul National University has not only advanced the development of exoskeleton technology but also brought new opportunities for practical applications.
For more information about exoskeleton applications, please visit: Exoskeleton Motor
