Why Are We Obsessed with Humanoid Robots?
In every video about humanoid robots, people often ask: "Why the obsession with researching humanoid robots? Can't bipedal, quadrupedal, or wheeled robots better adapt to work environments?"
Humanoid robots are designed to be closer to humans, allowing them to use existing environments and tools, such as household appliances and workplaces. This design makes them more naturally integrated into human environments. Additionally, they can use natural language and non-verbal communication methods (like gestures and facial expressions) to interact with humans more naturally. This type of interaction is especially valuable in fields like service, caregiving, and education, and is something other robots can't easily replace.
From simple mechanical devices to modern advanced robots with high intelligence and complex interaction abilities, the technology of humanoid robots has continuously progressed. Here are some significant robots in the history of humanoid robot development, and predictions for their future direction:
WABOT-1 (1973)
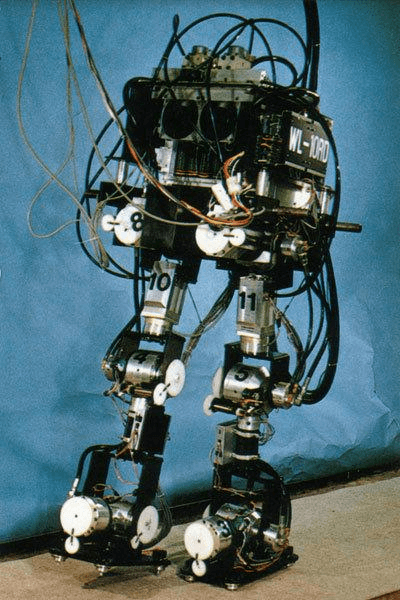
WABOT-1, developed by Waseda University in Japan in 1973, was the world’s first full-sized humanoid robot. It used an electric drive system and had basic movement and object-grabbing abilities. WABOT-1 could interact with humans through simple voice commands and used photoelectric sensors to recognize objects and measure distances, marking the transition from mechanical devices to robots with preliminary intelligence.
ASIMO (2000)
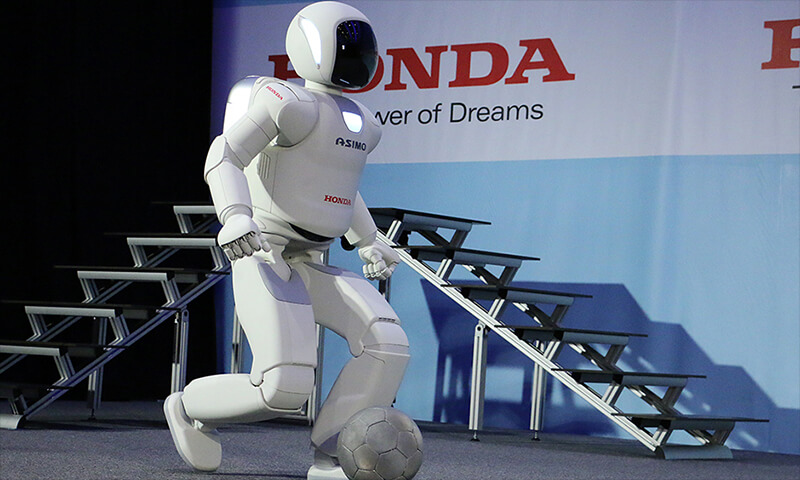
ASIMO, introduced by Honda in 2000, was a highly flexible humanoid robot, with its name being an acronym for "Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility." ASIMO used servo motors for driving and was capable of walking, running, and climbing stairs. It could interact with humans naturally through voice and gesture recognition systems, and could express emotions through nods and gestures, showcasing significant advances in interaction capabilities.
Atlas (2013)
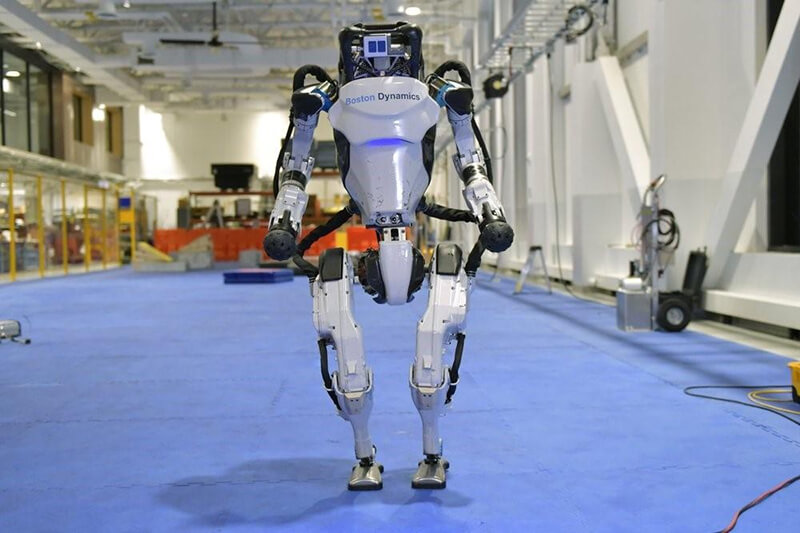

Atlas, developed by Boston Dynamics and first unveiled in 2013, is a highly complex advanced humanoid robot. It uses a hydraulic drive system and can walk, run, and perform high-difficulty actions such as flips and jumps on various terrains. Its design is aimed at addressing rescue missions in hazardous environments, with sensors and algorithms enabling real-time environmental perception and execution of complex tasks.
Sophia (2016)
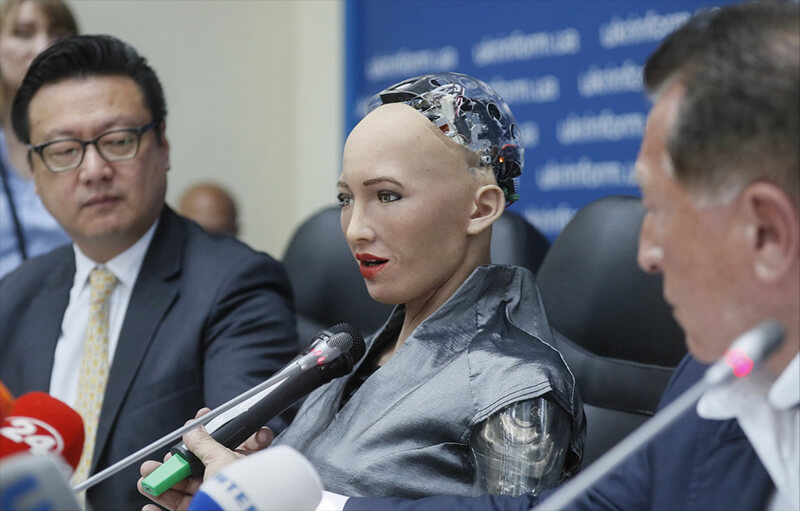

Sophia, launched by Hanson Robotics in 2016, is a social humanoid robot. Sophia uses electric servo systems to drive its facial "muscles," allowing her to display a wide range of complex facial expressions and engage in conversations using natural language processing technology. She can understand and respond to human emotional states, making interactions more natural and genuine.
Tesla Bot (2024)
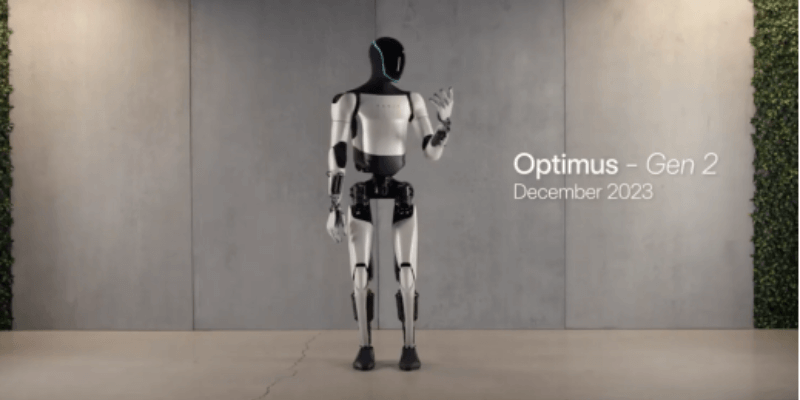
The latest Tesla Bot, introduced in 2024, is designed to handle repetitive, dangerous, or monotonous tasks. It uses an electric drive system with flexible movement capabilities and leverages AI and sensor technology to perceive and analyze the environment in real-time. It can automatically complete various tasks based on voice commands and collaborate with other devices.
The Evolution of Humanoid Robots
From the simple mechanical device of WABOT-1 in 1973 to the advanced Tesla Bot in 2024, humanoid robots have evolved significantly, from basic object manipulation to complex task execution. Future humanoid robots may exhibit impressive capabilities in the following areas:
Advanced Intelligence and Natural Interaction: They may achieve higher levels of intelligence and natural interaction, such as engaging in deep conversations using advanced natural language processing and emotional analysis technologies, and understanding and responding to complex emotional needs.
Enhanced Autonomy and Flexibility: Future robots might have greater autonomy, enabling them to perform complex tasks independently and collaborate seamlessly with other robots or intelligent devices.
Physical Capabilities and Applications: They could possess exceptional flexibility and strong physical capabilities, performing tasks ranging from high-precision operations to extreme sports, and finding widespread application in fields like healthcare, education, home assistance, and emergency rescue.
Future robots will not just be tools for performing tasks but will become highly intelligent and emotionally interactive companions, integral assistants in human lives. This direction will expand their roles in various fields while also introducing new ethical and legal challenges, requiring a balance between technological innovation and societal norms.
